5G NR
This module provides layers and functions to support simulations of 5G NR compliant features, in particular, the physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH). It provides implementations of a subset of the physical layer functionalities as described in the 3GPP specifications [3GPP38211], [3GPP38212], and [3GPP38214].
The best way to discover this module’s components is by having a look at the 5G NR PUSCH Tutorial.
The following code snippet shows how you can make standard-compliant simulations of the 5G NR PUSCH with a few lines of code:
# Create a PUSCH configuration with default settings
pusch_config = PUSCHConfig()
# Instantiate a PUSCHTransmitter from the PUSCHConfig
pusch_transmitter = PUSCHTransmitter(pusch_config)
# Create a PUSCHReceiver using the PUSCHTransmitter
pusch_receiver = PUSCHReceiver(pusch_transmitter)
# AWGN channel
channel = AWGN()
# Simulate transmissions over the AWGN channel
batch_size = 16
no = 0.1 # Noise variance
x, b = pusch_transmitter(batch_size) # Generate transmit signal and info bits
y = channel([x, no]) # Simulate channel output
b_hat = pusch_receiver([y, no]) # Recover the info bits
# Compute BER
print("BER:", compute_ber(b, b_hat).numpy())
The PUSCHTransmitter and PUSCHReceiver provide high-level abstractions of all required processing blocks. You can easily modify them according to your needs.
Carrier
CarrierConfig
- class sionna.nr.CarrierConfig(**kwargs)[source]
The CarrierConfig objects sets parameters for a specific OFDM numerology, as described in Section 4 [3GPP38211].
All configurable properties can be provided as keyword arguments during the initialization or changed later.
Example
>>> carrier_config = CarrierConfig(n_cell_id=41) >>> carrier_config.subcarrier_spacing = 30
- property cyclic_prefix
Cyclic prefix length
The option “normal” corresponds to 14 OFDM symbols per slot, while “extended” corresponds to 12 OFDM symbols. The latter option is only possible with a subcarrier_spacing of 60 kHz.
- Type:
str, “normal” (default) | “extended”
- property cyclic_prefix_length
Cyclic prefix length \(N_{\text{CP},l}^{\mu} \cdot T_{\text{c}}\) [s]
- Type:
float, read-only
- property frame_duration
Duration of a frame \(T_\text{f}\) [s]
- Type:
float, 10e-3 (default), read-only
- property frame_number
System frame number \(n_\text{f}\)
- Type:
int, 0 (default), [0,…,1023]
- property kappa
The constant \(\kappa = T_\text{s}/T_\text{c}\)
- Type:
float, 64, read-only
- property mu
Subcarrier spacing configuration, \(\Delta f = 2^\mu 15\) kHz
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6, read-only
- property n_cell_id
Physical layer cell identity \(N_\text{ID}^\text{cell}\)
- Type:
int, 1 (default) | [0,…,1007]
- property n_size_grid
Number of resource blocks in the carrier resource grid \(N^{\text{size},\mu}_{\text{grid},x}\)
- Type:
int, 4 (default) | [1,…,275]
- property n_start_grid
Start of resource grid relative to common resource block (CRB) 0 \(N^{\text{start},\mu}_{\text{grid},x}\)
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | [0,…,2199]
- property num_slots_per_frame
Number of slots per frame \(N_\text{slot}^{\text{frame},\mu}\)
Depends on the subcarrier_spacing.
- Type:
int, 10 (default) | 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 | 320 | 640, read-only
- property num_slots_per_subframe
Number of slots per subframe \(N_\text{slot}^{\text{subframe},\mu}\)
Depends on the subcarrier_spacing.
- Type:
int, 1 (default) | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64, read-only
- property num_symbols_per_slot
Number of OFDM symbols per slot \(N_\text{symb}^\text{slot}\)
Configured through the cyclic_prefix.
- Type:
int, 14 (default) | 12, read-only
- property slot_number
Slot number within a frame \(n^\mu_{s,f}\)
- Type:
int, 0 (default), [0,…,num_slots_per_frame]
- property sub_frame_duration
Duration of a subframe \(T_\text{sf}\) [s]
- Type:
float, 1e-3 (default), read-only
- property subcarrier_spacing
Subcarrier spacing \(\Delta f\) [kHz]
- Type:
float, 15 (default) | 30 | 60 | 120 | 240 | 480 | 960
- property t_c
Sampling time \(T_\text{c}\) for subcarrier spacing 480kHz.
- Type:
float, 0.509e-9 [s], read-only
- property t_s
Sampling time \(T_\text{s}\) for subcarrier spacing 15kHz.
- Type:
float, 32.552e-9 [s], read-only
Layer Mapping
LayerMapper
- class sionna.nr.LayerMapper(num_layers=1, verbose=False, **kwargs)[source]
Performs MIMO layer mapping of modulated symbols to layers as defined in [3GPP38211].
The LayerMapper supports PUSCH and PDSCH channels and follows the procedure as defined in Sec. 6.3.1.3 and Sec. 7.3.1.3 in [3GPP38211], respectively.
As specified in Tab. 7.3.1.3.-1 [3GPP38211], the LayerMapper expects two input streams for multiplexing if more than 4 layers are active (only relevant for PDSCH).
The class inherits from the Keras layer class and can be used as layer in a Keras model.
- Parameters:
num_layers (int, 1 (default) | [1,...,8]) – Number of MIMO layers. If
num_layers>=4, a list of two inputs is expected.verbose (bool, False (default)) – If True, additional parameters are printed.
- Input:
inputs ([…,n], or [[…,n1], […,n2]], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the sequence of symbols to be mapped. If
num_layers>=4, a list of two inputs is expected and n1/n2 must be chosen as defined in Tab. 7.3.1.3.-1 [3GPP38211].- Output:
[…,num_layers, n/num_layers], tf.complex – 2+D tensor containing the sequence of symbols mapped to the MIMO layers.
- property num_codewords
Number of input codewords for layer mapping. Can be either 1 or 2.
- property num_layers
Number of MIMO layers
- property num_layers0
Number of layers for first codeword (only relevant for num_codewords =2)
- property num_layers1
Number of layers for second codeword (only relevant for num_codewords =2)
LayerDemapper
- class sionna.nr.LayerDemapper(layer_mapper, num_bits_per_symbol=1, **kwargs)[source]
Demaps MIMO layers to coded transport block(s) by following Sec. 6.3.1.3 and Sec. 7.3.1.3 in [3GPP38211].
This layer must be associated to a
LayerMapperand performs the inverse operation.It is assumed that
num_bits_per_symbolconsecutive LLRs belong to a single symbol position. This allows to apply the LayerDemapper after demapping symbols to LLR values.If the layer mapper is configured for dual codeword transmission, a list of both transport block streams is returned.
The class inherits from the Keras layer class and can be used as layer in a Keras model.
- Parameters:
layer_mapper (
LayerMapper) – Associated LayerMapper.num_bits_per_symbol (int, 1 (default)) – Modulation order. Defines how many consecutive LLRs are associated to the same symbol position.
- Input:
inputs ([…,num_layers, n/num_layers], tf.float) – 2+D tensor containing MIMO layer data sequences.
- Output:
[…,n], or [[…,n1], […,n2]], tf.float – 2+D tensor containing the sequence of bits after layer demapping. If
num_codewords=2, a list of two transport blocks is returned.
Note
As it is more convenient to apply the layer demapper after demapping symbols to LLRs, this layer groups the input sequence into groups of
num_bits_per_symbolLLRs before restoring the original symbol sequence. This behavior can be deactivated by settingnum_bits_per_symbol=1.
PUSCH
PUSCHConfig
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHConfig(carrier_config=None, pusch_dmrs_config=None, tb_config=None, **kwargs)[source]
The PUSCHConfig objects sets parameters for a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH), as described in Sections 6.3 and 6.4 [3GPP38211].
All configurable properties can be provided as keyword arguments during the initialization or changed later.
- Parameters:
carrier_config (
CarrierConfigor None) – An instance ofCarrierConfig. If None, aCarrierConfiginstance with default settings will be created.pusch_dmrs_config (
PUSCHDMRSConfigor None) – An instance ofPUSCHDMRSConfig. If None, aPUSCHDMRSConfiginstance with default settings will be created.
Example
>>> pusch_config = PUSCHConfig(mapping_type="B") >>> pusch_config.dmrs.config_type = 2 >>> pusch_config.carrier.subcarrier_spacing = 30
- c_init(l)[source]
Compute RNG initialization \(c_\text{init}\) as in Section 6.4.1.1.1.1 [3GPP38211]
- Input:
l (int) – OFDM symbol index relative to a reference \(l\)
- Output:
c_init (int) – RNG initialization value
- property carrier
Carrier configuration
- Type:
- property dmrs
PUSCH DMRS configuration
- Type:
- property dmrs_grid
Empty resource grid for each DMRS port, filled with DMRS signals
This property returns for each configured DMRS port an empty resource grid filled with DMRS signals as defined in Section 6.4.1.1 [3GPP38211]. Not all possible options are implemented, e.g., frequency hopping and transform precoding are not available.
This property provides the unprecoded DMRS for each configured DMRS port. Precoding might be applied to map the DMRS to the antenna ports. However, in this case, the number of DMRS ports cannot be larger than the number of layers.
- Type:
complex, [num_dmrs_ports, num_subcarriers, num_symbols_per_slot], read-only
- property dmrs_mask
Masked resource elements in the resource grid. True corresponds to resource elements on which no data is transmitted.
- Type:
bool, [num_subcarriers, num_symbols_per_slot], read-only
- property dmrs_symbol_indices
Indices of DMRS symbols within a slot
- Type:
list, int, read-only
- property frequency_hopping
Frequency hopping configuration
- Type:
str, “neither” (default), read-only
- property l_bar
List of possible values of \(\bar{l}\) used for DMRS generation
Defined in Tables 6.4.1.1.3-3 and 6.4.1.1.3-4 [3GPP38211].
- Type:
list, elements in [0,…,11], read-only
- property mapping_type
Mapping type
- Type:
string, “A” (default) | “B”
- property n_rnti
Radio network temporary identifier \(n_\text{RNTI}\)
- Type:
int, 1 (default), [0,…,65535]
- property n_size_bwp
Number of resource blocks in the bandwidth part (BWP) \(N^{\text{size},\mu}_{\text{BWP},i}\)
If set to None, the property
n_size_gridof carrier will be used.- Type:
int, None (default), [1,…,275]
- property n_start_bwp
Start of BWP relative to common resource block (CRB) 0 \(N^{\text{start},\mu}_{\text{BWP},i}\)
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | [0,…,2199]
- property num_antenna_ports
Number of antenna ports
Must be larger than or equal to
num_layers.- Type:
int, 1 (default) | 2 | 4
- property num_coded_bits
Number of coded bits that fit into one PUSCH slot.
- Type:
int, read-only
- property num_layers
Number of transmission layers \(\nu\)
Must be smaller than or equal to
num_antenna_ports.- Type:
int, 1 (default) | 2 | 3 | 4
- property num_ov
Number of unused resource elements due to additional overhead as specified by higher layer.
- Type:
int, 0 (default), read-only
- property num_res_per_prb
Number of resource elements per PRB available for data
- Type:
int, read-only
- property num_resource_blocks
Number of allocated resource blocks for the PUSCH transmissions.
- Type:
int, read-only
- property num_subcarriers
Number of allocated subcarriers for the PUSCH transmissions
- Type:
int, read-only
- property precoding
PUSCH transmission scheme
- Type:
str, “non-codebook” (default), “codebook”
- property precoding_matrix
Precoding matrix \(\mathbf{W}\) as defined in Tables 6.3.1.5-1 to 6.3.1.5-7 [3GPP38211].
Only relevant if
precodingis “codebook”.- Type:
nd_array, complex, [num_antenna_ports, numLayers]
- property symbol_allocation
PUSCH symbol allocation
The first elements denotes the start of the symbol allocation. The second denotes the positive number of allocated OFDM symbols. For mapping_type “A”, the first element must be zero. For mapping_type “B”, the first element must be in [0,…,13]. The second element must be such that the index of the last allocated OFDM symbol is not larger than 13 (for “normal” cyclic prefix) or 11 (for “extended” cyclic prefix).
- Type:
2-tuple, int, [0, 14] (default)
- property tb_size
Transport block size, i.e., how many information bits can be encoded into a slot for the given slot configuration.
- Type:
int, read-only
- property tpmi
Transmit precoding matrix indicator
The allowed value depends on the number of layers and the number of antenna ports according to Table 6.3.1.5-1 until Table 6.3.1.5-7 [3GPP38211].
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | [0,…,27]
- property transform_precoding
Use transform precoding
- Type:
bool, False (default)
PUSCHDMRSConfig
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHDMRSConfig(**kwargs)[source]
The PUSCHDMRSConfig objects sets parameters related to the generation of demodulation reference signals (DMRS) for a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH), as described in Section 6.4.1.1 [3GPP38211].
All configurable properties can be provided as keyword arguments during the initialization or changed later.
Example
>>> dmrs_config = PUSCHDMRSConfig(config_type=2) >>> dmrs_config.additional_position = 1
- property additional_position
Maximum number of additional DMRS positions
The actual number of used DMRS positions depends on the length of the PUSCH symbol allocation.
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | 1 | 2 | 3
- property allowed_dmrs_ports
List of nominal antenna ports
The maximum number of allowed antenna ports max_num_dmrs_ports depends on the DMRS config_type and length. It can be equal to 4, 6, 8, or 12.
- Type:
list, [0,…,max_num_dmrs_ports-1], read-only
- property beta
Ratio of PUSCH energy per resource element (EPRE) to DMRS EPRE \(\beta^{\text{DMRS}}_\text{PUSCH}\) Table 6.2.2-1 [3GPP38214]
- Type:
float, read-only
- property cdm_groups
List of CDM groups \(\lambda\) for all ports in the dmrs_port_set as defined in Table 6.4.1.1.3-1 or 6.4.1.1.3-2 [3GPP38211]
Depends on the config_type.
- Type:
list, elements in [0,1,2], read-only
- property config_type
DMRS configuration type
The configuration type determines the frequency density of DMRS signals. With configuration type 1, six subcarriers per PRB are used for each antenna port, with configuration type 2, four subcarriers are used.
- Type:
int, 1 (default) | 2
- property deltas
List of delta (frequency) shifts \(\Delta\) for all ports in the port_set as defined in Table 6.4.1.1.3-1 or 6.4.1.1.3-2 [3GPP38211]
Depends on the config_type.
- Type:
list, elements in [0,1,2,4], read-only
- property dmrs_port_set
List of used DMRS antenna ports
The elements in this list must all be from the list of allowed_dmrs_ports which depends on the config_type as well as the length. If set to [], the port set will be equal to [0,…,num_layers-1], where
num_layersis a property of the parentPUSCHConfiginstance.- Type:
list, [] (default) | [0,…,11]
- property length
Number of front-loaded DMRS symbols A value of 1 corresponds to “single-symbol” DMRS, a value of 2 corresponds to “double-symbol” DMRS.
- Type:
int, 1 (default) | 2
- property n_id
Scrambling identities
Defines the scrambling identities \(N_\text{ID}^0\) and \(N_\text{ID}^1\) as a 2-tuple of integers. If None, the property
n_cell_idof theCarrierConfigis used.- Type:
2-tuple, None (default), [[0,…,65535], [0,…,65535]]
- property n_scid
DMRS scrambling initialization \(n_\text{SCID}\)
- Type:
int, 0 (default) | 1
- property num_cdm_groups_without_data
Number of CDM groups without data
This parameter controls how many REs are available for data transmission in a DMRS symbol. It should be greater or equal to the maximum configured number of CDM groups. A value of 1 corresponds to CDM group 0, a value of 2 corresponds to CDM groups 0 and 1, and a value of 3 corresponds to CDM groups 0, 1, and 2.
- Type:
int, 2 (default) | 1 | 3
- property type_a_position
Position of first DMRS OFDM symbol
Defines the position of the first DMRS symbol within a slot. This parameter only applies if the property
mapping_typeofPUSCHConfigis equal to “A”.- Type:
int, 2 (default) | 3
- property w_f
Frequency weight vectors \(w_f(k')\) for all ports in the port set as defined in Table 6.4.1.1.3-1 or 6.4.1.1.3-2 [3GPP38211]
- Type:
matrix, elements in [-1,1], read-only
- property w_t
Time weight vectors \(w_t(l')\) for all ports in the port set as defined in Table 6.4.1.1.3-1 or 6.4.1.1.3-2 [3GPP38211]
- Type:
matrix, elements in [-1,1], read-only
PUSCHLSChannelEstimator
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHLSChannelEstimator(resource_grid, dmrs_length, dmrs_additional_position, num_cdm_groups_without_data, interpolation_type='nn', interpolator=None, dtype=tf.complex64, **kwargs)[source]
Layer implementing least-squares (LS) channel estimation for NR PUSCH Transmissions.
After LS channel estimation at the pilot positions, the channel estimates and error variances are interpolated accross the entire resource grid using a specified interpolation function.
The implementation is similar to that of
LSChannelEstimator. However, it additional takes into account the separation of streams in the same CDM group as defined inPUSCHDMRSConfig. This is done through frequency and time averaging of adjacent LS channel estimates.- Parameters:
resource_grid (ResourceGrid) – An instance of
ResourceGriddmrs_length (int, [1,2]) – Length of DMRS symbols. See
PUSCHDMRSConfig.dmrs_additional_position (int, [0,1,2,3]) – Number of additional DMRS symbols. See
PUSCHDMRSConfig.num_cdm_groups_without_data (int, [1,2,3]) – Number of CDM groups masked for data transmissions. See
PUSCHDMRSConfig.interpolation_type (One of ["nn", "lin", "lin_time_avg"], string) – The interpolation method to be used. It is ignored if
interpolatoris not None. Available options areNearestNeighborInterpolator(“nn”) orLinearInterpolatorwithout (“lin”) or with averaging across OFDM symbols (“lin_time_avg”). Defaults to “nn”.interpolator (BaseChannelInterpolator) – An instance of
BaseChannelInterpolator, such asLMMSEInterpolator, or None. In the latter case, the interpolator specified byinterpolation_typeis used. Otherwise, theinterpolatoris used andinterpolation_typeis ignored. Defaults to None.dtype (tf.Dtype) – Datatype for internal calculations and the output dtype. Defaults to tf.complex64.
- Input:
(y, no) – Tuple:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size], tf.complex) – Observed resource grid
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] or only the first n>=0 dims, tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
h_ls ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size], tf.complex) – Channel estimates across the entire resource grid for all transmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_ls, tf.float) – Channel estimation error variance across the entire resource grid for all transmitters and streams
PUSCHPilotPattern
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHPilotPattern(pusch_configs, dtype=tf.complex64)[source]
Class defining a pilot pattern for NR PUSCH.
This class defines a
PilotPatternthat is used to configure an OFDMResourceGrid.For every transmitter, a separte
PUSCHConfigneeds to be provided from which the pilot pattern will be created.- Parameters:
pusch_configs (instance or list of
PUSCHConfig) – PUSCH Configurations according to which the pilot pattern will created. One configuration is needed for each transmitter.dtype (tf.Dtype) – Defines the datatype for internal calculations and the output dtype. Defaults to tf.complex64.
- property mask
Mask of the pilot pattern
- property normalize
Returns or sets the flag indicating if the pilots are normalized or not
- property num_data_symbols
Number of data symbols per transmit stream.
- property num_effective_subcarriers
Number of effectvie subcarriers
- property num_ofdm_symbols
Number of OFDM symbols
- property num_pilot_symbols
Number of pilot symbols per transmit stream.
- property num_streams_per_tx
Number of streams per transmitter
- property num_tx
Number of transmitters
- property pilots
Returns or sets the possibly normalized tensor of pilot symbols. If pilots are normalized, the normalization will be applied after new values for pilots have been set. If this is not the desired behavior, turn normalization off.
- show(tx_ind=None, stream_ind=None, show_pilot_ind=False)
Visualizes the pilot patterns for some transmitters and streams.
- Input:
tx_ind (list, int) – Indicates the indices of transmitters to be included. Defaults to None, i.e., all transmitters included.
stream_ind (list, int) – Indicates the indices of streams to be included. Defaults to None, i.e., all streams included.
show_pilot_ind (bool) – Indicates if the indices of the pilot symbols should be shown.
- Output:
list (matplotlib.figure.Figure) – List of matplot figure objects showing each the pilot pattern from a specific transmitter and stream.
- property trainable
Returns if pilots are trainable or not
PUSCHPrecoder
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHPrecoder(precoding_matrices, dtype=tf.complex64, **kwargs)[source]
Precodes a batch of modulated symbols mapped onto a resource grid for PUSCH transmissions. Each transmitter is assumed to have its own precoding matrix.
- Parameters:
precoding_matrices (list, [num_tx, num_antenna_ports, num_layers]. tf.complex) – List of precoding matrices, one for each transmitter. All precoding matrices must have the same shape.
dtype (One of [tf.complex64, tf.complex128]) – Dtype of inputs and outputs. Defaults to tf.complex64.
- Input:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_layers, num_symbols_per_slot, num_subcarriers] – Batch of resource grids to be precoded
- Output:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_antenna_ports, num_symbols_per_slot, num_subcarriers] – Batch of precoded resource grids
PUSCHReceiver
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHReceiver(pusch_transmitter, channel_estimator=None, mimo_detector=None, tb_decoder=None, return_tb_crc_status=False, stream_management=None, input_domain='freq', l_min=None, dtype=tf.complex64, **kwargs)[source]
This layer implements a full receiver for batches of 5G NR PUSCH slots sent by multiple transmitters. Inputs can be in the time or frequency domain. Perfect channel state information can be optionally provided. Different channel estimatiors, MIMO detectors, and transport decoders can be configured.
The layer combines multiple processing blocks into a single layer as shown in the following figure. Blocks with dashed lines are optional and depend on the configuration.
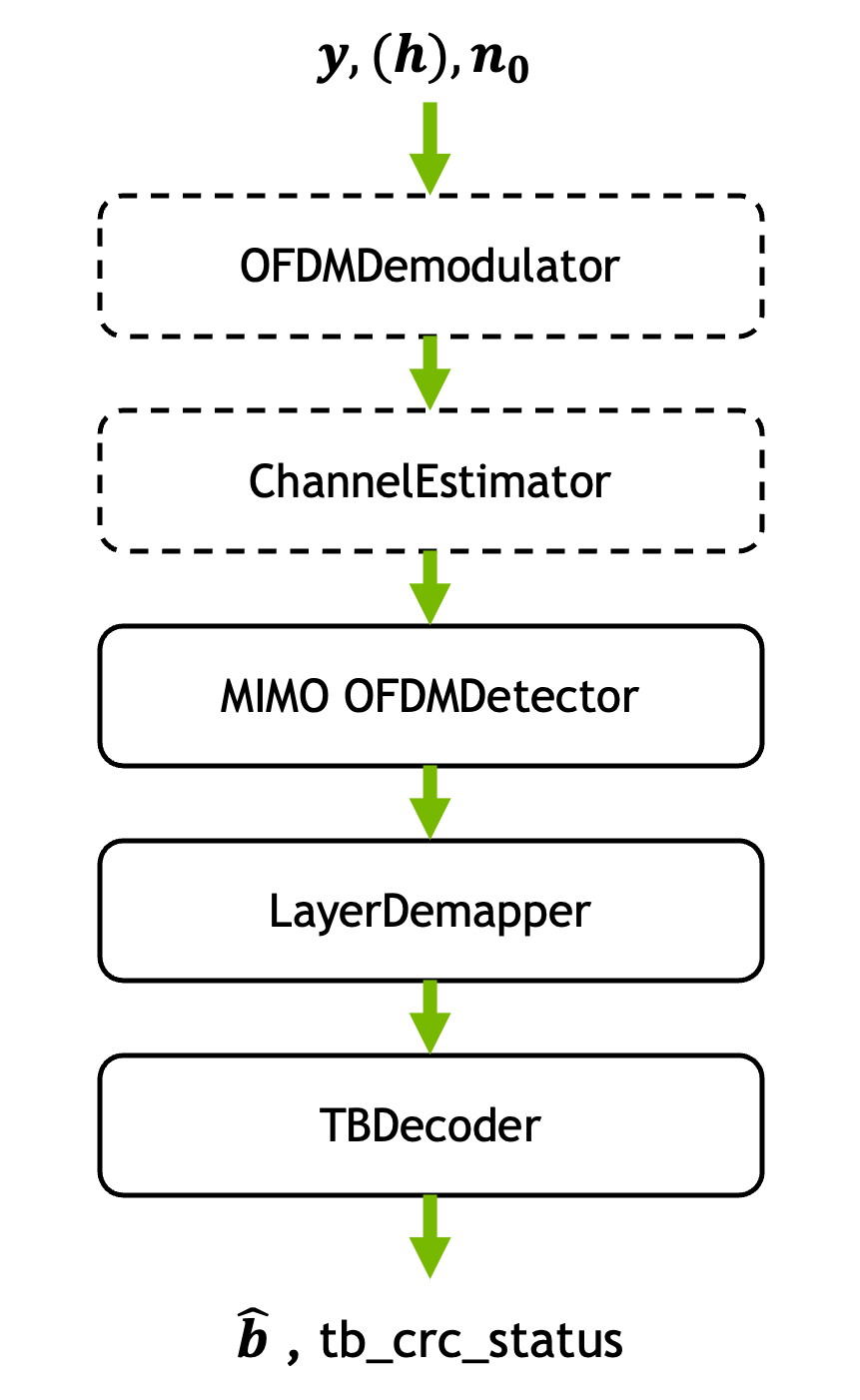
If the
input_domainequals “time”, the inputs \(\mathbf{y}\) are first transformed to resource grids with theOFDMDemodulator. Then channel estimation is performed, e.g., with the help of thePUSCHLSChannelEstimator. Ifchannel_estimatoris chosen to be “perfect”, this step is skipped and the input \(\mathbf{h}\) is used instead. Next, MIMO detection is carried out with an arbitraryOFDMDetector. The resulting LLRs for each layer are then combined to transport blocks with the help of theLayerDemapper. Finally, the transport blocks are decoded with theTBDecoder.- Parameters:
pusch_transmitter (
PUSCHTransmitter) – Transmitter used for the generation of the transmit signalschannel_estimator (
BaseChannelEstimator, “perfect”, or None) – Channel estimator to be used. If None, thePUSCHLSChannelEstimatorwith linear interpolation is used. If “perfect”, no channel estimation is performed and the channel state informationhmust be provided as additional input. Defaults to None.mimo_detector (
OFDMDetectoror None) – MIMO Detector to be used. If None, theLinearDetectorwith LMMSE detection is used. Defaults to None.tb_decoder (
TBDecoderor None) – Transport block decoder to be used. If None, theTBDecoderwith its default settings is used. Defaults to None.return_tb_crc_status (bool) – If True, the status of the transport block CRC is returned as additional output. Defaults to False.
stream_management (
StreamManagementor None) – Stream management configuration to be used. If None, it is assumed that there is a single receiver which decodes all streams of all transmitters. Defaults to None.input_domain (str, one of ["freq", "time"]) – Domain of the input signal. Defaults to “freq”.
l_min (int or None) – Smallest time-lag for the discrete complex baseband channel. Only needed if
input_domainequals “time”. Defaults to None.dtype (tf.Dtype) – Datatype for internal calculations and the output dtype. Defaults to tf.complex64.
- Input:
(y, h, no) – Tuple:
y ([batch size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size], tf.complex or [batch size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_time_samples + l_max - l_min], tf.complex) – Frequency- or time-domain input signal
h ([batch size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, num_subcarriers], tf.complex or [batch size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_time_samples + l_max - l_min, l_max - l_min + 1], tf.complex) – Perfect channel state information in either frequency or time domain (depending on
input_domain) to be used for detection. Only required ifchannel_estimatorequals “perfect”.no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] or only the first n>=0 dims, tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
b_hat ([batch_size, num_tx, tb_size], tf.float) – Decoded information bits
tb_crc_status ([batch_size, num_tx], tf.bool) – Transport block CRC status
Example
>>> pusch_config = PUSCHConfig() >>> pusch_transmitter = PUSCHTransmitter(pusch_config) >>> pusch_receiver = PUSCHReceiver(pusch_transmitter) >>> channel = AWGN() >>> x, b = pusch_transmitter(16) >>> no = 0.1 >>> y = channel([x, no]) >>> b_hat = pusch_receiver([x, no]) >>> compute_ber(b, b_hat) <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=0.0>
- property resource_grid
OFDM resource grid underlying the PUSCH transmissions
PUSCHTransmitter
- class sionna.nr.PUSCHTransmitter(pusch_configs, return_bits=True, output_domain='freq', dtype=tf.complex64, verbose=False, **kwargs)[source]
This layer generates batches of 5G NR PUSCH slots for multiple transmitters with random or provided payloads. Frequency- or time-domain outputs can be generated.
It combines multiple processing blocks into a single layer as shown in the following figure. Blocks with dashed lines are optional and depend on the configuration.
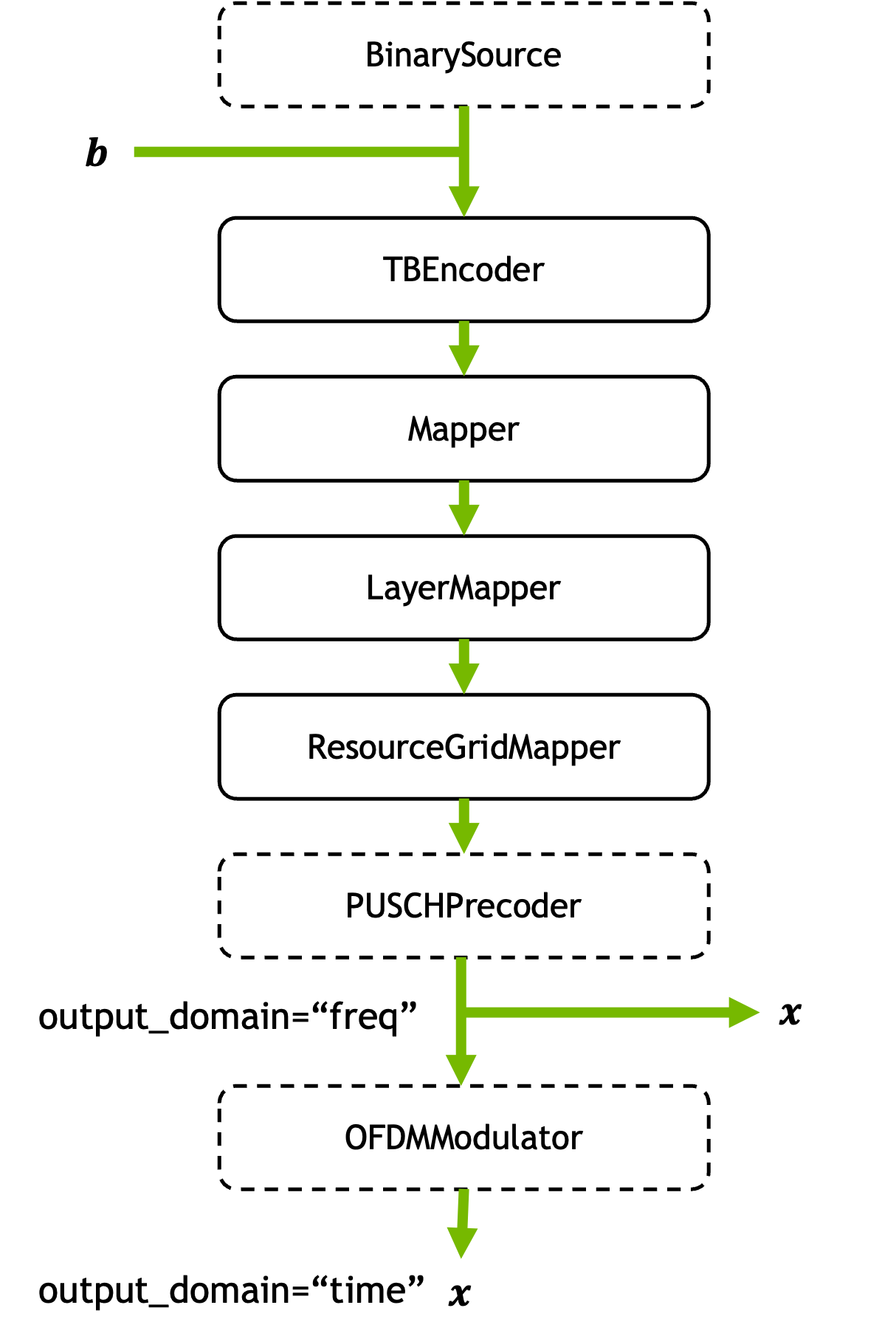
Information bits \(\mathbf{b}\) that are either randomly generated or provided as input are encoded into a transport block by the
TBEncoder. The encoded bits are then mapped to QAM constellation symbols by theMapper. TheLayerMappersplits the modulated symbols into different layers which are then mapped onto OFDM resource grids by theResourceGridMapper. If precoding is enabled in thePUSCHConfig, the resource grids are further precoded so that there is one for each transmitter and antenna port. Ifoutput_domainequals “freq”, these are the outputs \(\mathbf{x}\). Ifoutput_domainis chosen to be “time”, the resource grids are transformed into time-domain signals by theOFDMModulator.- Parameters:
pusch_configs (instance or list of
PUSCHConfig) – PUSCH Configurations according to which the resource grid and pilot pattern will created. One configuration is needed for each transmitter.return_bits (bool) – If set to True, the layer generates random information bits to be transmitted and returns them together with the transmit signal. Defaults to True.
output_domain (str, one of ["freq", "time"]) – The domain of the output. Defaults to “freq”.
dtype (One of [tf.complex64, tf.complex128]) – Dtype of inputs and outputs. Defaults to tf.complex64.
verbose (bool) – If True, additional parameters are printed during initialization. Defaults to False.
- Input:
One of
batch_size (int) – Batch size of random transmit signals to be generated, if
return_bitsis True.b ([batch_size, num_tx, tb_size], tf.float) – Information bits to be transmitted, if
return_bitsis False.
- Output:
x ([batch size, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size], tf.complex or [batch size, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_time_samples], tf.complex) – Transmit signal in either frequency or time domain, depending on
output_domain.b ([batch_size, num_tx, tb_size], tf.float) – Transmitted information bits. Only returned if
return_bitsis True.
Example
>>> pusch_config = PUSCHConfig() >>> pusch_transmitter = PUSCHTransmitter(pusch_config) >>> x, b = pusch_transmitter(16) >>> print("Shape of x:", x.shape) Shape of x: (16, 1, 1, 14, 48) >>> print("Shape of b:", b.shape) Shape of b: (16, 1, 1352)
- property pilot_pattern
Aggregate pilot pattern of all transmitters
- property resource_grid
OFDM resource grid underlying the PUSCH transmissions
Transport Block
TBConfig
- class sionna.nr.TBConfig(**kwargs)[source]
The TBConfig objects sets parameters related to the transport block encoding, as described in TS 38.214 [3GPP38214].
All configurable properties can be provided as keyword arguments during the initialization or changed later.
The TBConfig is configured by selecting the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) tables and index.
Example
>>> tb_config = TBConfig(mcs_index=13) >>> tb_config.mcs_table = 3 >>> tb_config.channel_type = "PUSCH" >>> tb_config.show()
The following tables provide an overview of the corresponding coderates and modulation orders.
Table 1 MCS Index Table 1 (Table 5.1.3.1-1 in [3GPP38214]) MCS Index\(I_{MCS}\)Modulation Order\(Q_m\)Target Coderate\(R\times[1024]\)Spectral Efficiency0
2
120
0.2344
1
2
157
0.3066
2
2
193
0.3770
3
2
251
0.4902
4
2
308
0.6016
5
2
379
0.7402
6
2
449
0.8770
7
2
526
1.0273
8
2
602
1.1758
9
2
679
1.3262
10
4
340
1.3281
11
4
378
1.4766
12
4
434
1.6953
13
4
490
1.9141
14
4
553
2.1602
15
4
616
2.4063
16
4
658
2.5703
17
6
438
2.5664
18
6
466
2.7305
19
6
517
3.0293
20
6
567
3.3223
21
6
616
3.6094
22
6
666
3.9023
23
6
719
4.2129
24
6
772
4.5234
25
6
822
4.8164
26
6
873
5.1152
27
6
910
5.3320
28
6
948
5.5547
Table 2 MCS Index Table 2 (Table 5.1.3.1-2 in [3GPP38214]) MCS Index\(I_{MCS}\)Modulation Order\(Q_m\)Target Coderate\(R\times[1024]\)Spectral Efficiency0
2
120
0.2344
1
2
193
0.3770
2
2
308
0.6016
3
2
449
0.8770
4
2
602
1.1758
5
4
378
1.4766
6
4
434
1.6953
7
4
490
1.9141
8
4
553
2.1602
9
4
616
2.4063
10
4
658
2.5703
11
6
466
2.7305
12
6
517
3.0293
13
6
567
3.3223
14
6
616
3.6094
15
6
666
3.9023
16
6
719
4.2129
17
6
772
4.5234
18
6
822
4.8164
19
6
873
5.1152
20
8
682.5
5.3320
21
8
711
5.5547
22
8
754
5.8906
23
8
797
6.2266
24
8
841
6.5703
25
8
885
6.9141
26
8
916.5
7.1602
27
8
948
7.4063
Table 3 MCS Index Table 3 (Table 5.1.3.1-3 in [3GPP38214]) MCS Index\(I_{MCS}\)Modulation Order\(Q_m\)Target Coderate\(R\times[1024]\)Spectral Efficiency0
2
30
0.0586
1
2
40
0.0781
2
2
50
0.0977
3
2
64
0.1250
4
2
78
0.1523
5
2
99
0.1934
6
2
120
0.2344
7
2
157
0.3066
8
2
193
0.3770
9
2
251
0.4902
10
2
308
0.6016
11
2
379
0.7402
12
2
449
0.8770
13
2
526
1.0273
14
2
602
1.1758
15
4
340
1.3281
16
4
378
1.4766
17
4
434
1.6953
18
4
490
1.9141
19
4
553
2.1602
20
4
616
2.4063
21
6
438
2.5564
22
6
466
2.7305
23
6
517
3.0293
24
6
567
3.3223
25
6
616
3.6094
26
6
666
3.9023
27
6
719
4.2129
28
6
772
4.5234
Table 4 MCS Index Table 4 (Table 5.1.3.1-4 in [3GPP38214]) MCS Index\(I_{MCS}\)Modulation Order\(Q_m\)Target Coderate\(R\times[1024]\)Spectral Efficiency0
2
120
0.2344
1
2
193
0.3770
2
2
449
0.8770
3
4
378
1.4766
4
4
490
1.9141
5
4
616
2.4063
6
6
466
2.7305
7
6
517
3.0293
8
6
567
3.3223
9
6
616
3.6094
10
6
666
3.9023
11
6
719
4.2129
12
6
772
4.5234
13
6
822
4.8154
14
6
873
5.1152
15
8
682.5
5.3320
16
8
711
5.5547
17
8
754
5.8906
18
8
797
6.2266
19
8
841
6.5703
20
8
885
6.9141
21
8
916.5
7.1602
22
8
948
7.4063
23
10
805.5
7.8662
24
10
853
8.3301
25
10
900.5
8.7939
26
10
948
9.2578
- property channel_type
5G NR physical channel type. Valid choices are “PDSCH” and “PUSCH”.
- property mcs_index
Modulation and coding scheme (MCS) index (denoted as \(I_{MCS}\) in [3GPP38214])
- property mcs_table
Indicates which MCS table from [3GPP38214] to use. Starts with “1”.
- property n_id
Data scrambling initialization \(n_\text{ID}\). Data Scrambling ID related to cell id and provided by higher layer. If None, the
PUSCHConfigwill automatically set \(n_\text{ID}=N_\text{ID}^{cell}\).- Type:
int, None (default), [0, 1023]
- property num_bits_per_symbol
Modulation order as defined by the selected MCS
- Type:
int, read-only
- property target_coderate
Target coderate of the TB as defined by the selected MCS
- Type:
float, read-only
- property tb_scaling
TB scaling factor for PDSCH as defined in [3GPP38214] Tab. 5.1.3.2-2.
- Type:
float, 1. (default), read-only
TBEncoder
- class sionna.nr.TBEncoder(target_tb_size, num_coded_bits, target_coderate, num_bits_per_symbol, num_layers=1, n_rnti=1, n_id=1, channel_type="PUSCH", codeword_index=0, use_scrambler=True, verbose=False, output_dtype=tf.float32, **kwargs)[source]
5G NR transport block (TB) encoder as defined in TS 38.214 [3GPP38214] and TS 38.211 [3GPP38211]
The transport block (TB) encoder takes as input a transport block of information bits and generates a sequence of codewords for transmission. For this, the information bit sequence is segmented into multiple codewords, protected by additional CRC checks and FEC encoded. Further, interleaving and scrambling is applied before a codeword concatenation generates the final bit sequence. Fig. 1 provides an overview of the TB encoding procedure and we refer the interested reader to [3GPP38214] and [3GPP38211] for further details.
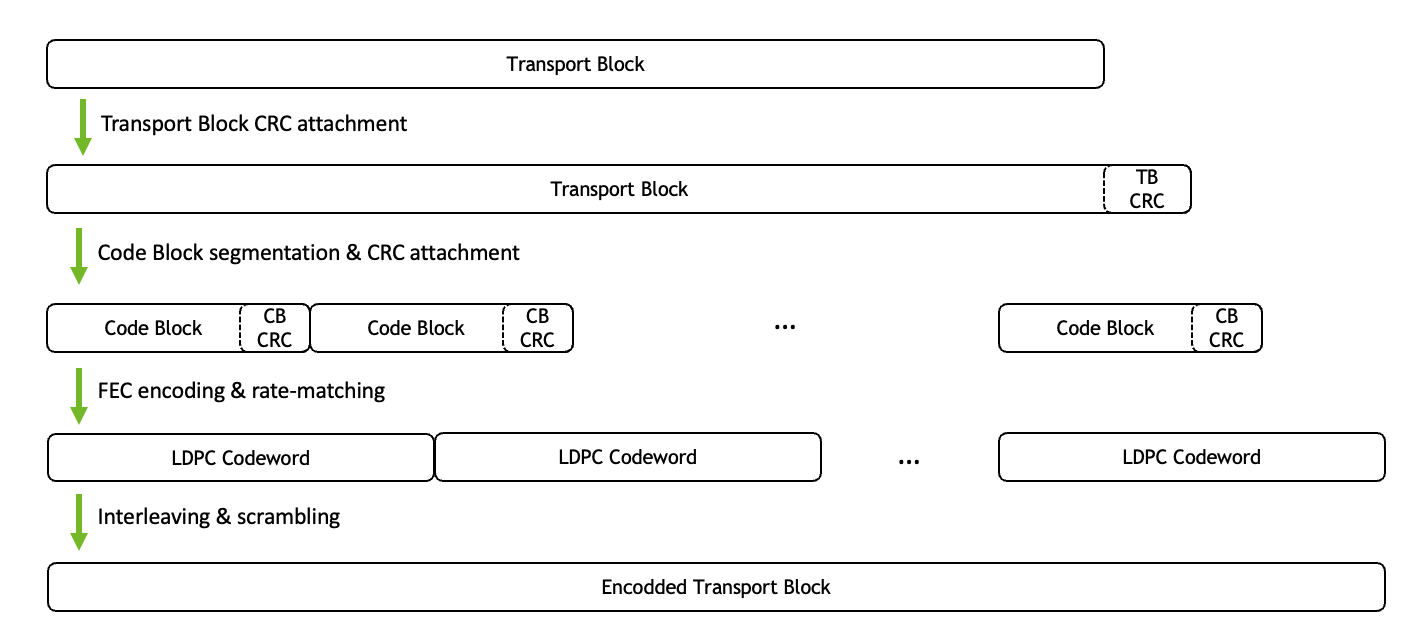
Fig. 13 Fig. 1: Overview TB encoding (CB CRC does not always apply).
If
n_rntiandn_idare given as list, the TBEncoder encodes num_tx = len(n_rnti) parallel input streams with different scrambling sequences per user.The class inherits from the Keras layer class and can be used as layer in a Keras model.
- Parameters:
target_tb_size (int) – Target transport block size, i.e., how many information bits are encoded into the TB. Note that the effective TB size can be slightly different due to quantization. If required, zero padding is internally applied.
num_coded_bits (int) – Number of coded bits after TB encoding.
target_coderate (float) – Target coderate.
num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Modulation order, i.e., number of bits per QAM symbol.
num_layers (int, 1 (default) | [1,...,8]) – Number of transmission layers.
n_rnti (int or list of ints, 1 (default) | [0,...,65335]) – RNTI identifier provided by higher layer. Defaults to 1 and must be in range [0, 65335]. Defines a part of the random seed of the scrambler. If provided as list, every list entry defines the RNTI of an independent input stream.
n_id (int or list of ints, 1 (default) | [0,...,1023]) – Data scrambling ID \(n_\text{ID}\) related to cell id and provided by higher layer. Defaults to 1 and must be in range [0, 1023]. If provided as list, every list entry defines the scrambling id of an independent input stream.
channel_type (str, "PUSCH" (default) | "PDSCH") – Can be either “PUSCH” or “PDSCH”.
codeword_index (int, 0 (default) | 1) – Scrambler can be configured for two codeword transmission.
codeword_indexcan be either 0 or 1. Must be 0 forchannel_type= “PUSCH”.use_scrambler (bool, True (default)) – If False, no data scrambling is applied (non standard-compliant).
verbose (bool, False (default)) – If True, additional parameters are printed during initialization.
dtype (tf.float32 (default)) – Defines the datatype for internal calculations and the output dtype.
- Input:
inputs ([…,target_tb_size] or […,num_tx,target_tb_size], tf.float) – 2+D tensor containing the information bits to be encoded. If
n_rntiandn_idare a list of size num_tx, the input must be of shape […,num_tx,target_tb_size].- Output:
[…,num_coded_bits], tf.float – 2+D tensor containing the sequence of the encoded codeword bits of the transport block.
Note
The parameters
tb_sizeandnum_coded_bitscan be derived by thecalculate_tb_size()function or by accessing the correspondingPUSCHConfigattributes.- property cb_crc_encoder
CB CRC encoder. None if no CB CRC is applied.
- property coderate
Effective coderate of the TB after rate-matching including overhead for the CRC.
- property cw_lengths
Each list element defines the codeword length of each of the codewords after LDPC encoding and rate-matching. The total number of coded bits is \(\sum\) cw_lengths.
- property k
Number of input information bits. Equals tb_size except for zero padding of the last positions if the
target_tb_sizeis quantized.
- property k_padding
Number of zero padded bits at the end of the TB.
- property ldpc_encoder
LDPC encoder used for TB encoding.
- property n
Total number of output bits.
- property num_cbs
Number code blocks.
- property num_tx
Number of independent streams
- property output_perm_inv
Inverse interleaver pattern for output bit interleaver.
- property scrambler
Scrambler used for TB scrambling. None if no scrambler is used.
- property tb_crc_encoder
TB CRC encoder
- property tb_size
Effective number of information bits per TB. Note that (if required) internal zero padding can be applied to match the request exact
target_tb_size.
TBDecoder
- class sionna.nr.TBDecoder(encoder, num_bp_iter=20, cn_type='boxplus-phi', output_dtype=tf.float32, **kwargs)[source]
5G NR transport block (TB) decoder as defined in TS 38.214 [3GPP38214].
The transport block decoder takes as input a sequence of noisy channel observations and reconstructs the corresponding transport block of information bits. The detailed procedure is described in TS 38.214 [3GPP38214] and TS 38.211 [3GPP38211].
The class inherits from the Keras layer class and can be used as layer in a Keras model.
- Parameters:
encoder (
TBEncoder) – Associated transport block encoder used for encoding of the signal.num_bp_iter (int, 20 (default)) – Number of BP decoder iterations
cn_type (str, "boxplus-phi" (default) | "boxplus" | "minsum") – The check node processing function of the LDPC BP decoder. One of {“boxplus”, “boxplus-phi”, “minsum”} where ‘“boxplus”’ implements the single-parity-check APP decoding rule. ‘“boxplus-phi”’ implements the numerical more stable version of boxplus [Ryan]. ‘“minsum”’ implements the min-approximation of the CN update rule [Ryan].
output_dtype (tf.float32 (default)) – Defines the datatype for internal calculations and the output dtype.
- Input:
inputs ([…,num_coded_bits], tf.float) – 2+D tensor containing channel logits/llr values of the (noisy) channel observations.
- Output:
b_hat ([…,target_tb_size], tf.float) – 2+D tensor containing hard decided bit estimates of all information bits of the transport block.
tb_crc_status ([…], tf.bool) – Transport block CRC status indicating if a transport block was (most likely) correctly recovered. Note that false positives are possible.
- property k
Number of input information bits. Equals TB size.
- property n
Total number of output codeword bits.
- property tb_size
Number of information bits per TB.
Utils
calculate_tb_size
- sionna.nr.utils.calculate_tb_size(modulation_order, target_coderate, target_tb_size=None, num_coded_bits=None, num_prbs=None, num_ofdm_symbols=None, num_dmrs_per_prb=None, num_layers=1, num_ov=0, tb_scaling=1.0, verbose=True)[source]
Calculates transport block (TB) size for given system parameters.
This function follows the basic procedure as defined in TS 38.214 Sec. 5.1.3.2 and Sec. 6.1.4.2 [3GPP38214].
- Parameters:
modulation_order (int) – Modulation order, i.e., number of bits per QAM symbol.
target_coderate (float) – Target coderate.
target_tb_size (None (default) | int) – Target transport block size, i.e., how many information bits can be encoded into a slot for the given slot configuration. If provided,
num_prbs,num_ofdm_symbolsandnum_dmrs_per_prbwill be ignored.num_coded_bits (None (default) | int) – How many coded bits can be fit into a given slot. If provided,
num_prbs,num_ofdm_symbolsandnum_dmrs_per_prbwill be ignored.num_prbs (None (default) | int) – Total number of allocated PRBs per OFDM symbol where 1 PRB equals 12 subcarriers.
num_ofdm_symbols (None (default) | int) – Number of OFDM symbols allocated for transmission. Cannot be larger than 14.
num_dmrs_per_prb (None (default) | int) – Number of DMRS (i.e., pilot) symbols per PRB that are NOT used for data transmission. Sum over all
num_ofdm_symbolsOFDM symbols.num_layers (int, 1 (default)) – Number of MIMO layers.
num_ov (int, 0 (default)) – Number of unused resource elements due to additional overhead as specified by higher layer.
tb_scaling (float, 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 (default)) – TB scaling factor for PDSCH as defined in TS 38.214 Tab. 5.1.3.2-2. Valid choices are 0.25, 0.5 and 1.0.
verbose (bool, False (default)) – If True, additional information will be printed.
- Returns:
(tb_size, cb_size, num_cbs, cw_length, tb_crc_length, cb_crc_length, cw_lengths) – Tuple:
tb_size (int) – Transport block size, i.e., how many information bits can be encoded into a slot for the given slot configuration.
cb_size (int) – Code block (CB) size. Determines the number of information bits (including TB/CB CRC parity bits) per codeword.
num_cbs (int) – Number of code blocks. Determines into how many CBs the TB is segmented.
cw_lengths (list of ints) – Each list element defines the codeword length of each of the
num_cbscodewords after LDPC encoding and rate-matching. The total number of coded bits is \(\sum\)cw_lengths.tb_crc_length (int) – Length of the TB CRC.
cb_crc_length (int) – Length of each CB CRC.
Note
Due to rounding,
cw_lengths(=length of each codeword after encoding), can be slightly different within a transport block. Thus,cw_lengthsis given as a list of ints where each list elements denotes the number of codeword bits of the corresponding codeword after rate-matching.
generate_prng_seq
- sionna.nr.utils.generate_prng_seq(length, c_init)[source]
Implements pseudo-random sequence generator as defined in Sec. 5.2.1 in [3GPP38211] based on a length-31 Gold sequence.
- Parameters:
length (int) – Desired output sequence length.
c_init (int) – Initialization sequence of the PRNG. Must be in the range of 0 to \(2^{32}-1\).
- Output:
[
length], ndarray of 0s and 1s – Containing the scrambling sequence.
Note
The initialization sequence
c_initis application specific and is usually provided be higher layer protocols.
select_mcs
- sionna.nr.utils.select_mcs(mcs_index, table_index=1, channel_type='PUSCH', transform_precoding=False, pi2bpsk=False, verbose=False)[source]
Selects modulation and coding scheme (MCS) as specified in TS 38.214 [3GPP38214].
Implements MCS tables as defined in [3GPP38214] for PUSCH and PDSCH.
- Parameters:
mcs_index (int| [0,...,28]) – MCS index (denoted as \(I_{MCS}\) in [3GPP38214]).
table_index (int, 1 (default) | 2 | 3 | 4) – Indicates which MCS table from [3GPP38214] to use. Starts with index “1”.
channel_type (str, "PUSCH" (default) | "PDSCH") – 5G NR physical channel type. Valid choices are “PDSCH” and “PUSCH”.
transform_precoding (bool, False (default)) – If True, the MCS tables as described in Sec. 6.1.4.1 in [3GPP38214] are applied. Only relevant for “PUSCH”.
pi2bpsk (bool, False (default)) – If True, the higher-layer parameter tp-pi2BPSK as described in Sec. 6.1.4.1 in [3GPP38214] is applied. Only relevant for “PUSCH”.
verbose (bool, False (default)) – If True, additional information will be printed.
- Returns:
(modulation_order, target_rate) – Tuple:
modulation_order (int) – Modulation order, i.e., number of bits per symbol.
target_rate (float) – Target coderate.